Golang Gin框架(三):模板语法专题
测试demo
动态加载页面
package api
import (
"net/http"
"path/filepath" "strings"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin")
// 动态加载templates下的页面
func searchHTMLTemplates() map[string]bool {
matches, _ := filepath.Glob("templates/*.html")
htmlBaseFilename := make(map[string]bool, len(matches))
for _, path := range matches {
filename := filepath.Base(path)
baseFilename := strings.Split(filename, ".")[0]
htmlBaseFilename[baseFilename] = true
}
return htmlBaseFilename
}
func LoadHTMLFiles(c *gin.Context) {
baseFilename := c.DefaultQuery("file", "index") // 获取GET参数
baseFilename = strings.TrimSpace(strings.ToLower(baseFilename)) // 转小写并去除空白字符
validBaseFilename := searchHTMLTemplates()
ignoreInvalidTemplate := c.DefaultQuery("ignore", "true") == "true"
if !validBaseFilename[baseFilename] && !ignoreInvalidTemplate {
c.JSON(http.StatusNotFound, gin.H{
"error": "模板文件不存在",
})
return
}
filename := strings.Join([]string{baseFilename, ".html"}, "") // 动态渲染模板页面
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, filename, gin.H{})
}text/template模板语法
Gin框架模板也是以{{}}包裹模板语句
变量声明
- 变量名需以
$开头,如$variable - 采用与Go一致的变量声明语法:
- 即变量声明时使用
:=,而修改和访问变量时使用=;如{{$avr := "abc"}} - 变量必须先声明再使用
- 访问变量时也以
$开头,如{{$var}}
- 即变量声明时使用
<p>{{$var := "abc"}}<p>
<p>定义并渲染一个变量: {{$var}}</p><br>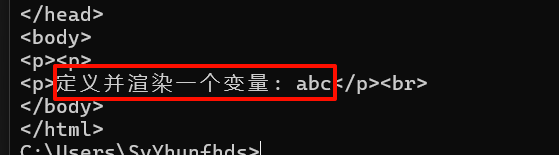
模板字面量
自己脑补大括号
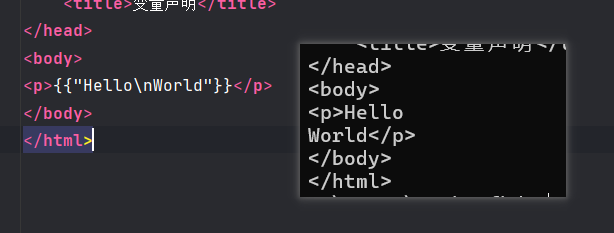
- 字符串:
"abc"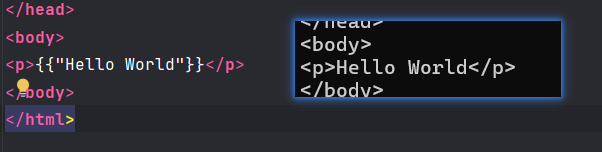
- 字节:
'a'(渲染为码点,即97)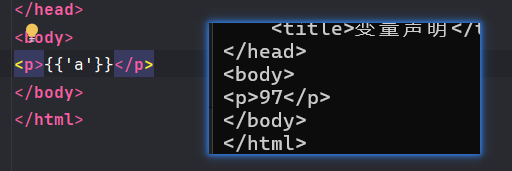
- 原始字符串:
a不会转义(用反引号包裹,这里是没法用反引号包裹反引号)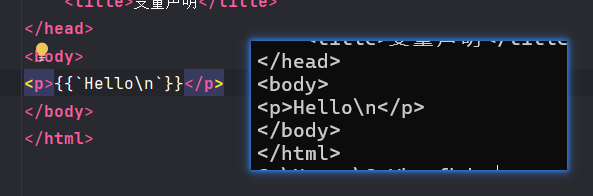
nil类型:print nil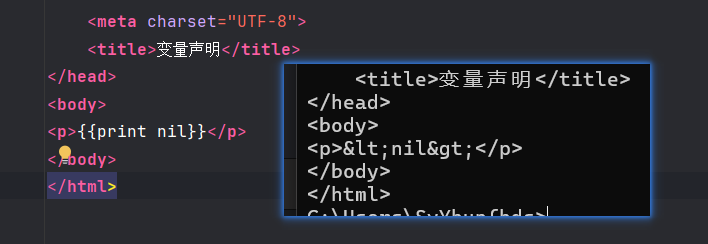
只有nil会报错: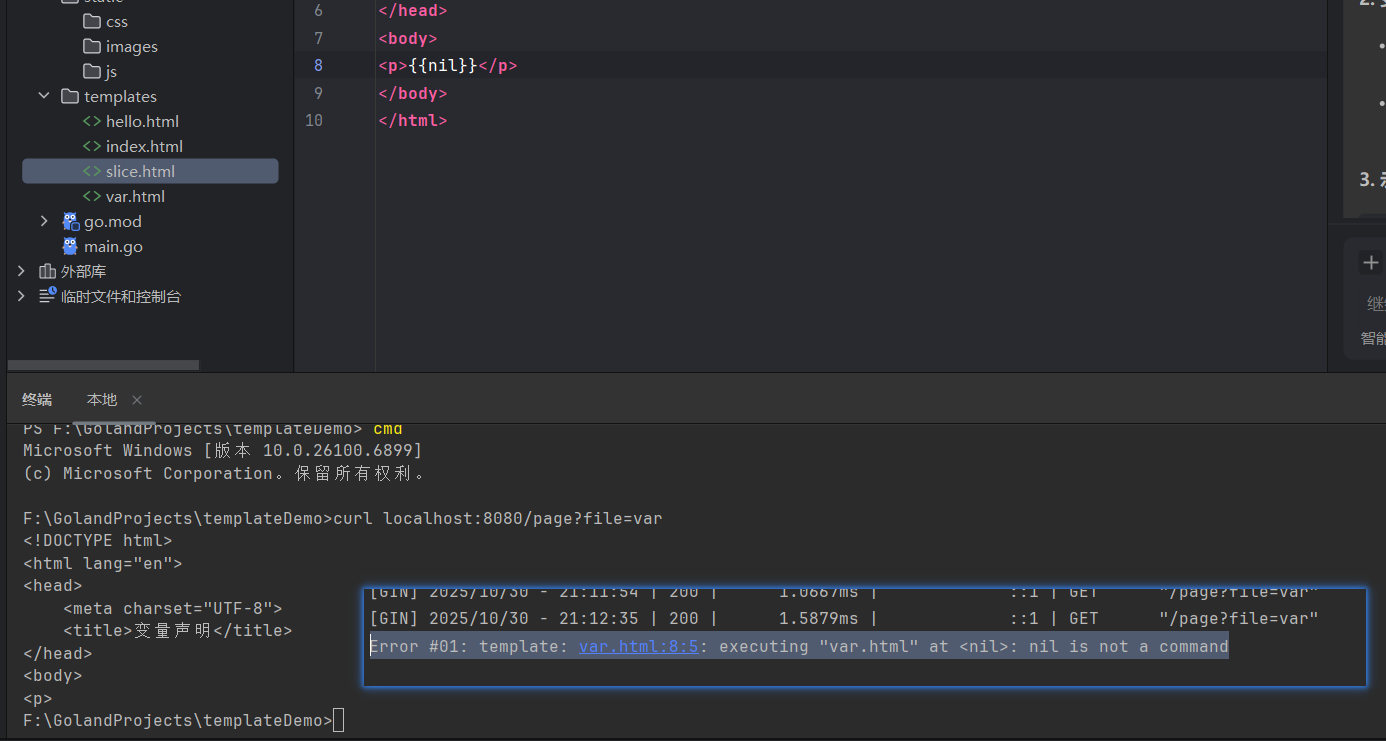
(在日志里报错)
上下文
.访问当前位置的上下文$引用当前模板根级的上下文$.引用模板中的根级上下文
这里的上下文指的是c.HTML的第三个参数所传入的键值对或结构体实例,而.号所访问的就是这个实例本身
控制结构
if-else条件结构
语法:
{{if eq .Number 1}}
数字等于1
{{else if eq .Number 2}}
数字等于2
{{else if gt .Number 2}}
数字大于2
{{else}}
其他情况
{{end}}常用模板函数:(顺便了解一下)
eq: 等于ne: 不等于lt: 小于le: 小于等于gt: 大于ge: 大于等于
由于Gin没有数学运算符,所以要想进行数学运算,需通过管道符
|和函数来实现,例:
{{range $key, $value := .Numbers}}
{{if $value}}
<p>数字 {{$key}} 是偶数</p>
{{else if eq ($key|mod 2) 1}}
<p>数字 {{$key}} 是奇数</p>
{{else}}
<p>数字 {{$key}} 的其他情况</p>
{{end}}
{{end}}示例:
func IfElseDemo(c *gin.Context) {
dataLenInQuery := c.DefaultQuery("num", "16")
// 转换为整型
dataLen, _ := strconv.Atoi(dataLenInQuery)
data := make(map[int]bool, dataLen)
for i := 0; i < dataLen; i++ {
num := rand.Int() % 10
data[num] = (num % 2) == 0
}
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "if-else.html", gin.H{
"Numbers": data,
})
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>if-else分支结构(奇偶判断)</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>if-else分支结构(奇偶判断)</h1>
{{range $num, $isEven := .Numbers}}
{{if $isEven}}
<p>{{$num}}是偶数</p>
{{else}}
<p>{{$num}}是奇数</p>
{{end}}
{{end}} <!-- 结束循环域 -->
</body>
</html>因为还不懂具体的else if怎么写,所以只能先用键值对代替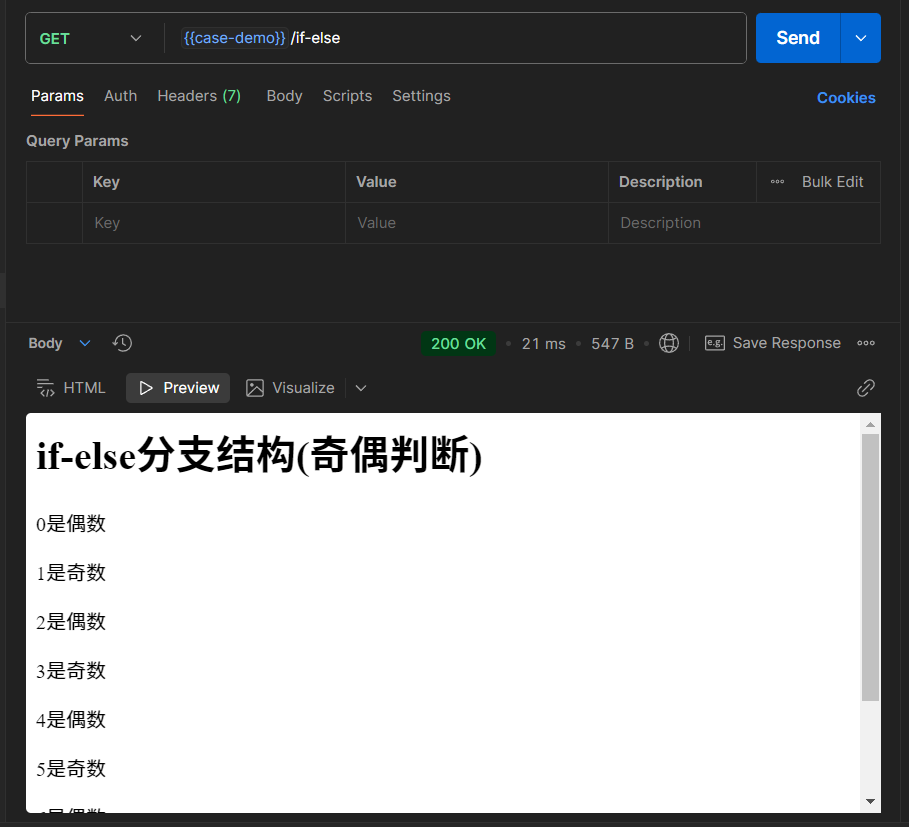
range遍历结构
语法和Go类似,但是range被置于变量前面:
// 自行脑补括号
{{range $index, $value := .Slice}} // 只要确保:=符号后面的复合结构是数组或切片即可
<p>{{$index}}索引的值为{{$value}}</p>
{{end}} // 记得结束作用域
// 键值对
{{range $key, $value := .Map}}
<p>{{$key}}键的值为{{$value}}</p>
{{end}}
// 通道
{{range .Channel}}
{{.}}
{{end}}range-else结构
转载自网络
range也支持else,当被range的数据长度为0时,执行else
{{/*range...else...*/}}
{{range .arr_num}}
{{.}}
{{else}}
{{0}} {{/*当.arr_num长度为0时,执行else*/}}
{{end}}with重定向结构
当传入模板的结构体或键值对含有多个字段时,老是打字段的前缀(键值对的一级键)会很烦。可以用with...end结构重定向.的上下文
示例:
<!-- 回到slice.html-->
<!-- 示例2:遍历产品列表 -->
<div class="section">
<div class="section-title">产品信息列表</div>
{{with .Products}} <!-- 这里换成with -->
{{range .}}
<div class="item-card">
<div class="item-title">产品详情</div>
{{range $key, $value := .}}
<div class="key-value-pair">
<span class="key">{{$key}}:</span>
<span class="value">{{$value}}</span>
</div>
{{end}}
</div>
{{end}}
{{end}} <!-- 结束with域 -->
</div>// API传入的实例不变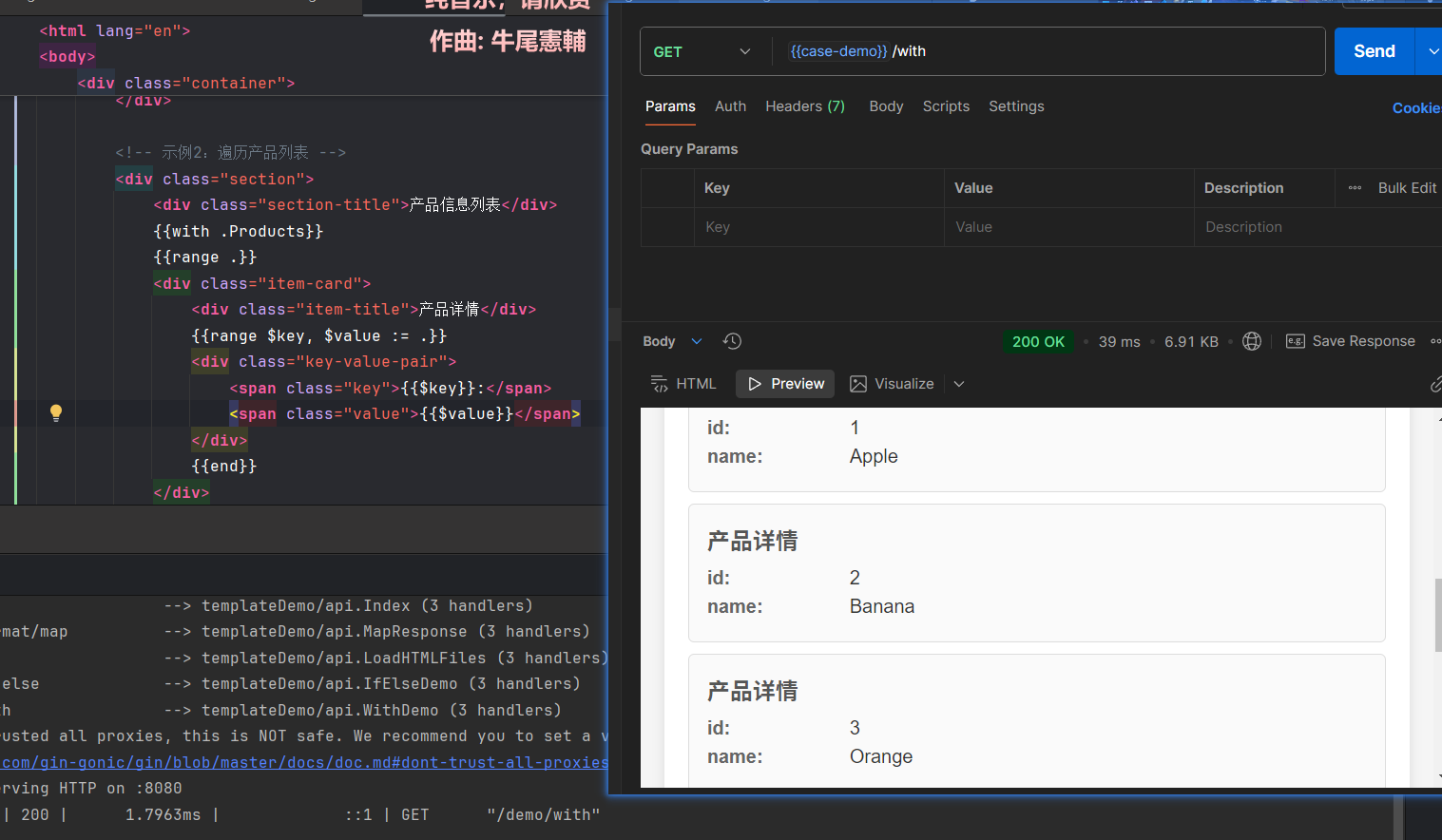
with-else结构
with也有else分支,遍历到没数据后就进入else分支了:(实例转载自网络)
{{/*with else方式*/}}
{{with .user_data}}
{{.Name}}
{{.Age}}
{{else}}
<p>无数据</p>
{{end}}range和with结构隐式改变上下文
在 range 和 with 结构内部,. 的含义会改变。
- 在
{{range .Items}}循环内部,. 就变成了Items中的单个元素。 - 在
{{with .User}}结构内部,. 就变成了.User对象。
此时,如果想访问最外层传进来的数据,就需要使用之前提到的根级上下文$。
template语句
{{template "模板名" pipeline}}
// 示例如下:
{{template "base.html" .}}示例:
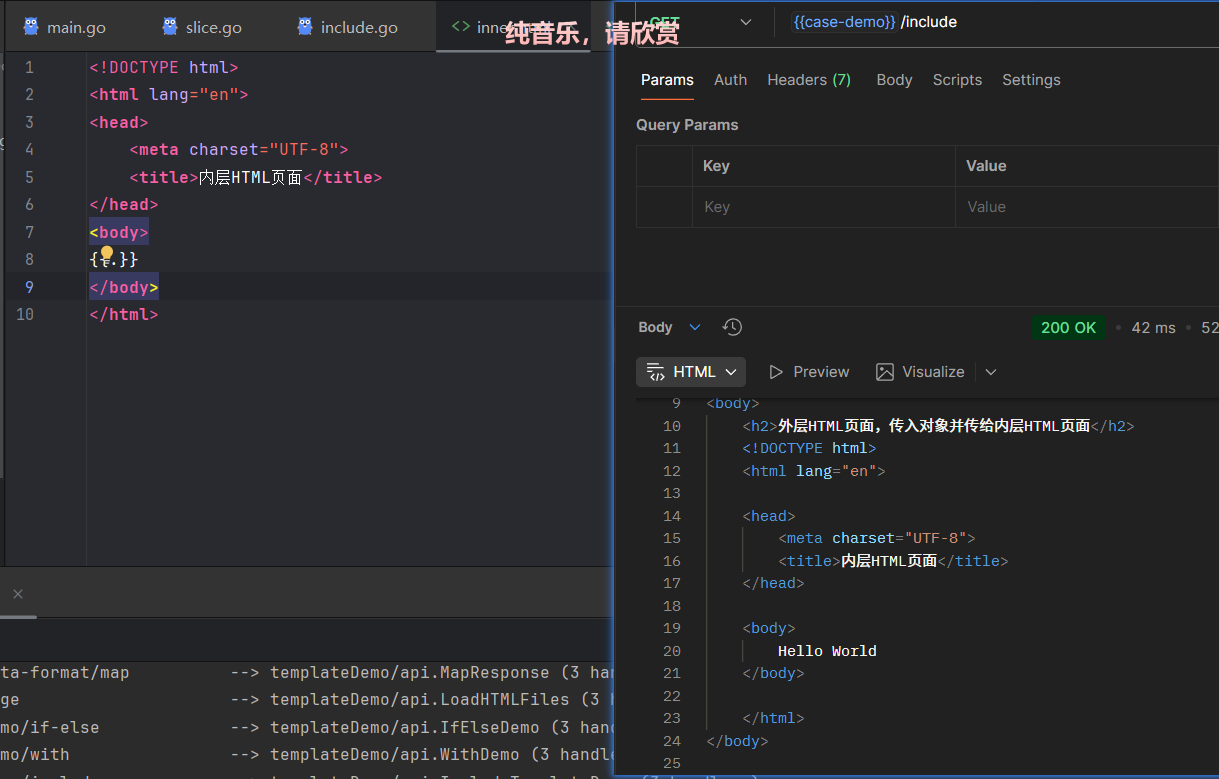
外层HTML:outer.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>外层HTML页面,传入对象并传给内层HTML页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>外层HTML页面,传入对象并传给内层HTML页面</h2>
{{template "inner.html" .Message}}
</body>
</html>内层HTML:inner.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>内层HTML页面</title>
</head>
<body>
{{.}}
</body>
</html>API:
package api
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
func IncludeTemplateDemo(c *gin.Context) {
message := "Hello World"
c.HTML(200, "outer.html", gin.H{
"Message": message,
})
}
模板函数 (AI)
管道符|
在 Go 模板中,管道符 | 用于将一个命令的输出作为另一个命令的输入,类似于 Unix shell 中的管道概念。
{{ expression | function }}单个函数管道
{{ .Name | upper }} <!-- 将 .Name 传递给 upper 函数 -->
{{ .Price | printf "$%.2f" }} <!-- 格式化价格 -->链式管道
{{ .Name | lower | title }} <!-- 先转小写再首字母大写 -->
{{ .Description | truncate 50 | html }} <!-- 截取50字符后转HTML -->与条件语句结合
{{ if .Count | gt 0 }}
有 {{ .Count }} 个项目
{{ end }}参数传递
{{ .Name | printf "Hello, %s!" }} <!-- 将 .Name 作为 printf 的第二个参数 -->
{{ .Items | len | printf "Total: %d items" }}在 range 中使用
{{ range .Items }}
<li>{{ . | upper }}</li>
{{ end }}管道符让模板代码更加简洁和易读,避免嵌套调用的复杂性。
print系列
Go 模板中的 print、printf 和 println 函数是内置函数,用于格式化输出:
1. print 函数
- 用途:格式化参数并返回字符串,不添加空格或换行
- 语法:
{{print arg1 arg2 ...}} - 示例:
{{print "Hello" "World"}} <!-- 输出: HelloWorld -->
{{print .Name " is " .Age " years old"}} <!-- 输出: Alice is 25 years old -->2. printf 函数
- 用途:根据格式字符串格式化参数,类似于 C 语言的
printf - 语法:
{{printf format arg1 arg2 ...}} - 示例:
{{printf "%s is %d years old" .Name .Age}} <!-- 输出: Alice is 25 years old -->
{{printf "Price: $%.2f" .Price}} <!-- 输出: Price: $12.34 -->3. println 函数
- 用途:格式化参数并在末尾添加换行符
- 语法:
{{println arg1 arg2 ...}} - 示例:
{{println "Hello" "World"}} <!-- 输出: Hello World\n -->
{{println .Name .Age}} <!-- 输出: Alice 25\n -->and、or、not函数
and: 从左到右,返回第一个为“空”(false, 0, nil, "", 空集合)的参数值;如果所有参数都不为空,则返回最后一个参数的值。or: 从左到右,返回第一个为“不为空”的参数值;如果所有参数都为空,则返回最后一个参数的值。not返回输入参数的否定值
也可以用来实现逻辑判断,但其返回值不一定是true或false,
示例(转载自网络):
...
func BoolFunc(ctx *gin.Context) {
data := map[string]interface{}{
"arr": [3]int{1, 2, 3},
"a": "hello",
}
ctx.HTML(http.StatusOK, "and_or_not_func.html", data)
}
......
{{/* and的用法 [1 2 3] */}}
{{and .a .arr}}
{{/* or的用法 hello */}}
{{or .a .arr}}
{{/* not的用法 false */}}
{{not .arr}}
...index、len
index读取指定类型对应下标的值,支持 map、slice、array、string类型index 索引 复合结构len返回对应类型的长度,支持map、slice、array、string、chan类型len 复合结构
。
示例:
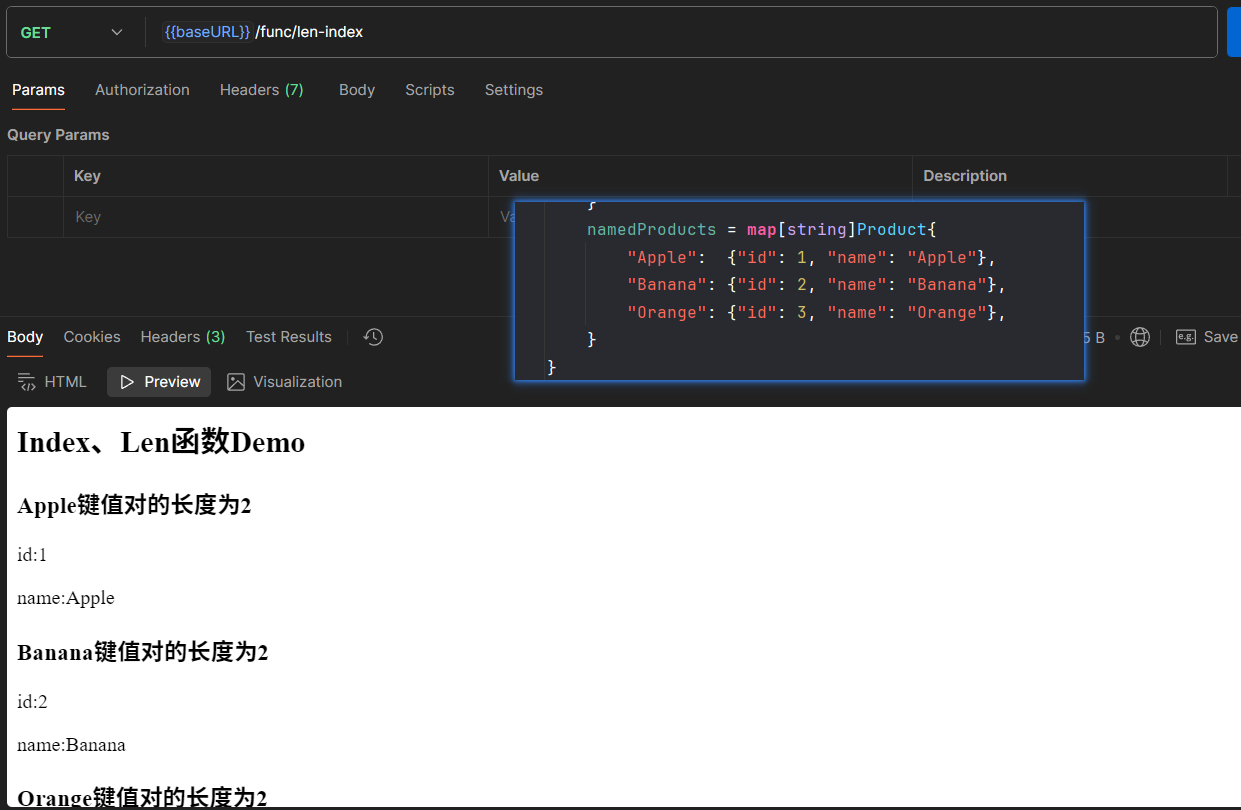
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Index、Len函数Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Index、Len函数Demo</h2>
{{range $firstKey, $valueMap := . }}
<h3>{{$firstKey}}键值对的长度为{{len $valueMap}}</h3>
{{range $secondKey, $value := $valueMap}}
<p>{{$secondKey}}:{{index $valueMap $secondKey}}</p>
{{end}}
{{end}}
</body>
</html>package api
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin")
func LenIndexDemo(c *gin.Context) {
data := namedProducts // 来自slice.go的map数据
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "len-index.html", data)
}
逻辑判断运算符
eq等于ne不等于lt小于le小于等于gt大于ge大于等于
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>eq等运算符演示Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>eq等运算符演示Demo</h2>
{{range $name, $age := .Persons}}
{{if le $age 18}}
<p>{{$name}}是青年人</p>
{{else if and (gt $age 18) (le $age 50)}}
<p>{{$name}}是中年人</p>
{{else}}
<p>{{$name}}是老年人</p>
{{end}}
{{end}}
</body>
</html>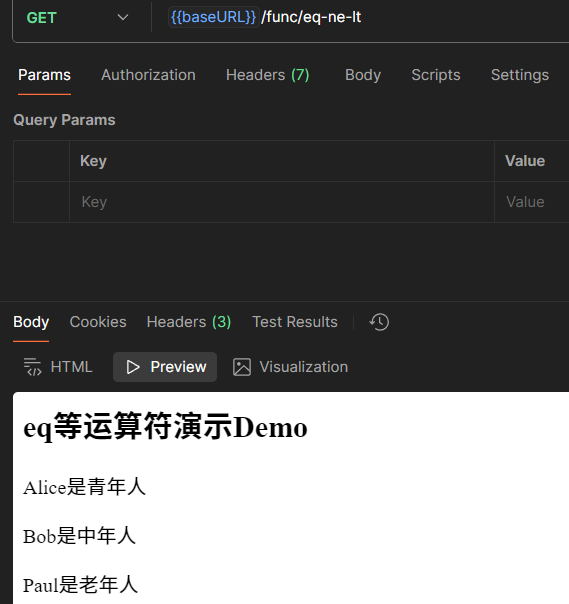
Format
这就是Go的函数,不是模板的函数……是在Go里用的,不是在模板里用的
示例(转载自网络):
...
func FormatFunc(ctx *gin.Context) {
now_time := time.Now().Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05")
ctx.HTML(http.StatusOK, "time_format_func.html", now_time)
}
......
{{.}}
...自定义模板函数
- 定义函数:
func add(a int, b int) int {
return a + b
}- 加入路由实例中:
...
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.SetFuncMap(template.FuncMap{
"Add": add, // 字符串名称前端使用
})
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.GET("/define_func", DefineFunc)
router.Run(":8080")
}
...- 前端使用:
...
{{Add 1 2}}
...text/template补充
text/template VS html/template
html/template会自动进行上下文感知的内容转义,以防止 XSS (跨站脚本) 攻击。text/template没有上述的特性,对于后端传入的XSS字符串,会原样输出,触发XSS漏洞
……
不过我测不出来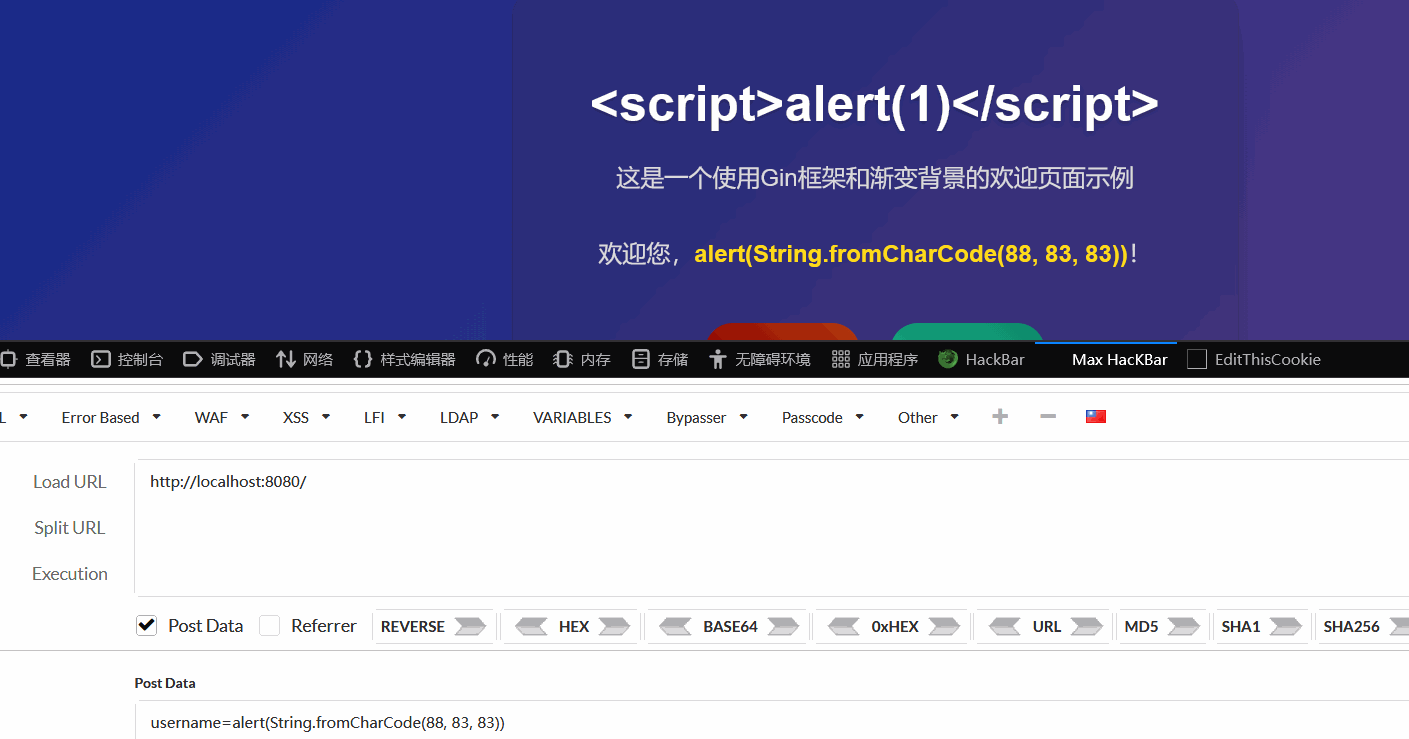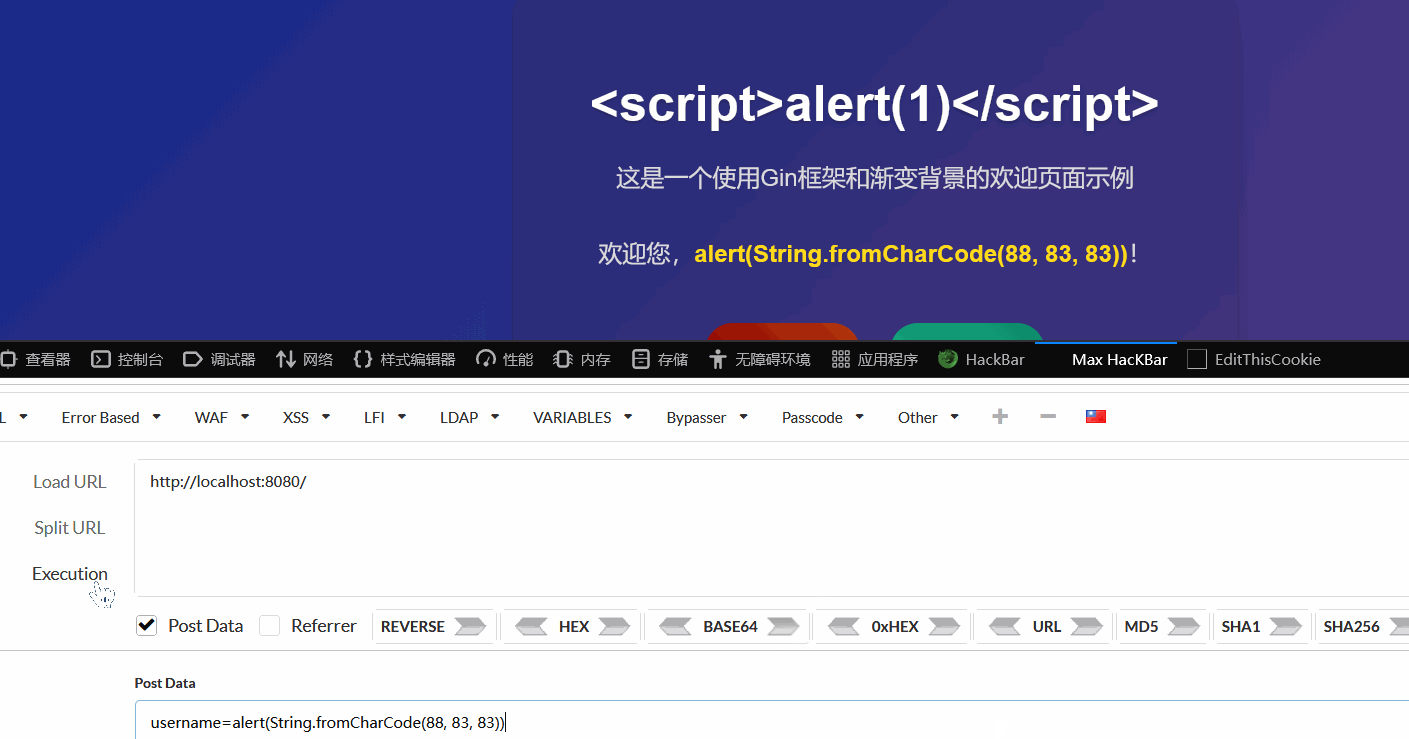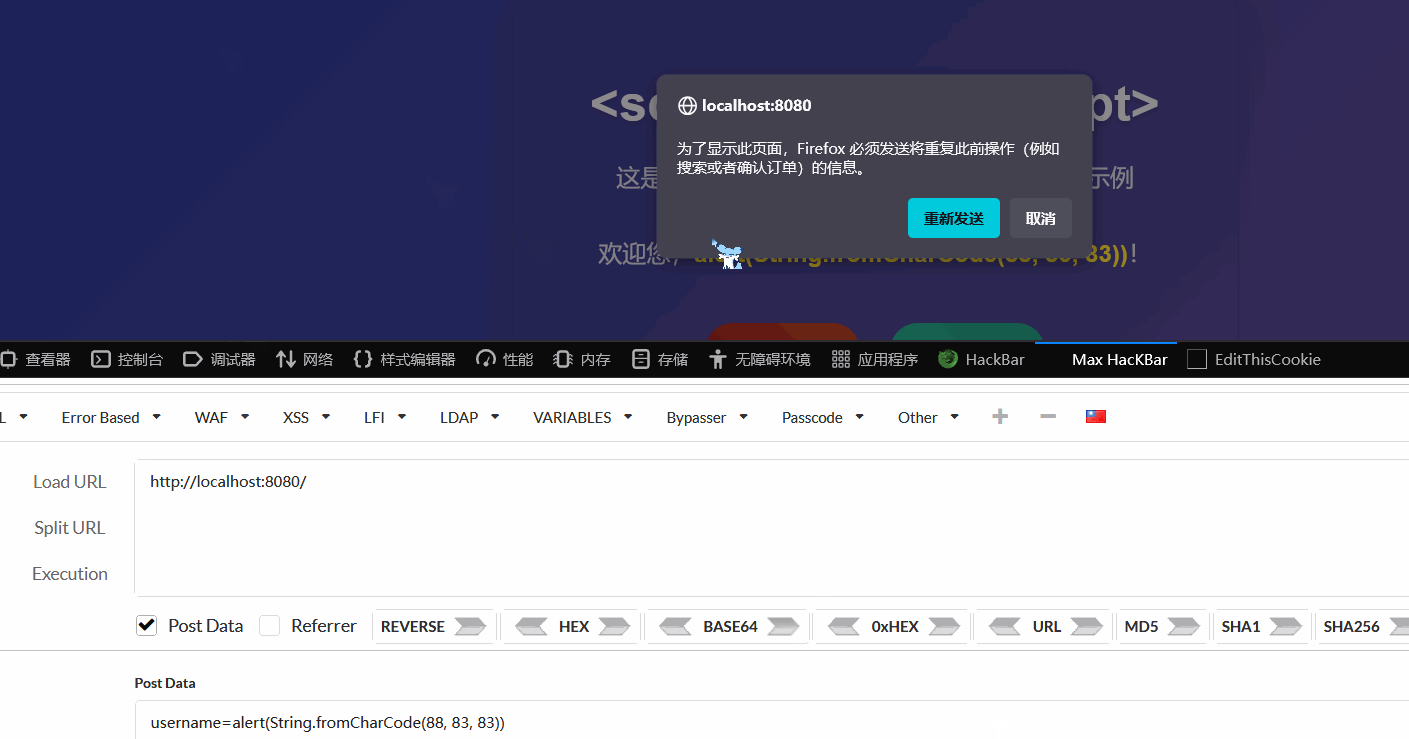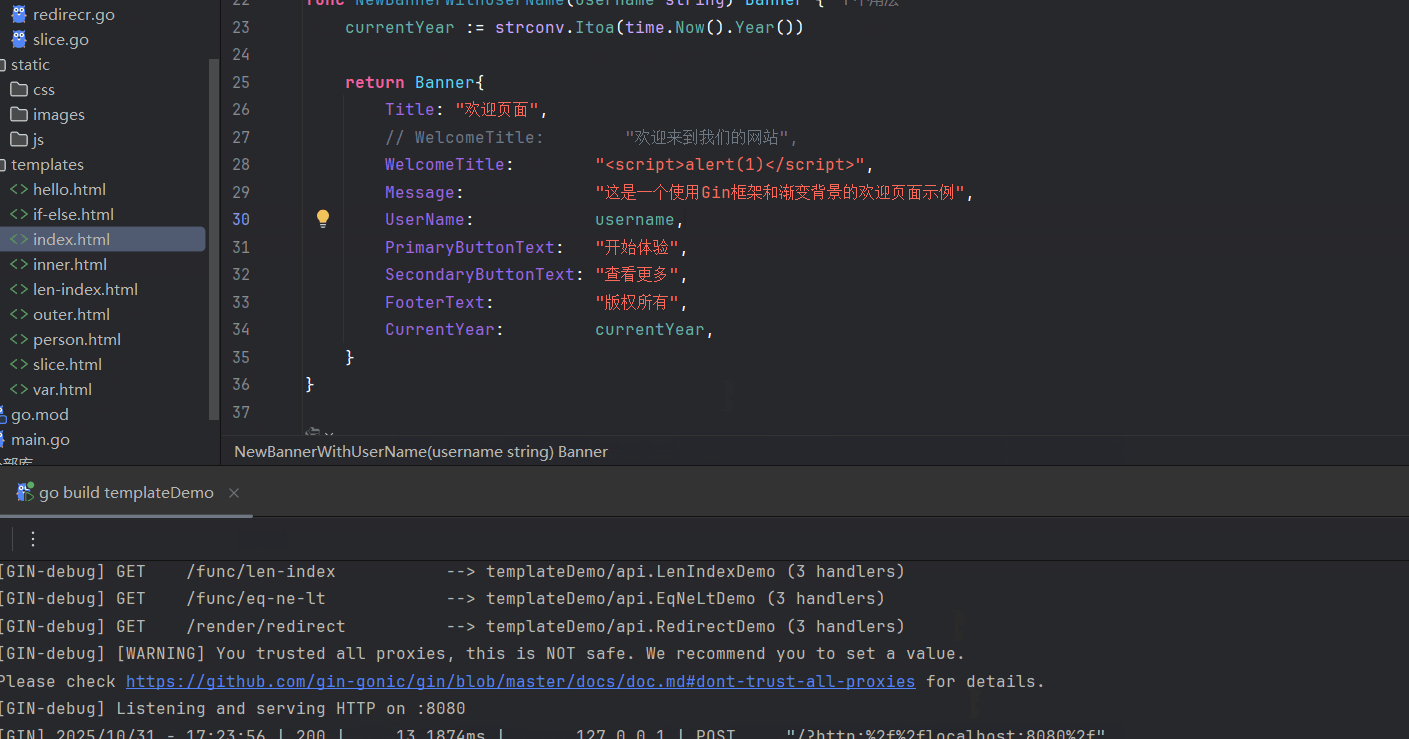
有必要时可以无视风险强行渲染 :
// Go 端
import "html/template"
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
// 告诉模板,这段 HTML 是安全的,请不要转义
"safeHTML": template.HTML("<p>This is a trusted paragraph.</p>"),
})
// 模板端
{{.safeHTML}} // 这段内容将作为原生 HTML 被渲染模板继承与组合
{{template "模板名" pipeline }}:加载其他模板{{define "模板名"}}...{{end}}:定义一个可被引用的模板片段。{{block "模板名" pipeline}}...{{end}}(更推荐):定义一个可被子模板覆盖的模板块。
示例:
layouts/base.html (父模板)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>{{block "title" .}}Default Title{{end}}</title>
</head>
<body>
<header>My Website Header</header>
<main>
{{block "content" .}}Default Content{{end}}
</main>
<footer>My Website Footer</footer>
</body>
</html>index.html (子模板)
{{/* 继承 base.html 布局 */}}
{{template "layouts/base.html" .}}
{{/* 定义/覆盖 title 块 */}}
{{define "title"}}Home Page{{end}}
{{/* 定义/覆盖 content 块 */}}
{{define "content"}}
<h1>Welcome to the Home Page!</h1>
<p>This is specific content for the index page.</p>
{{end}}移除多余换行字符
在前面的很多demo中都出现了源于range和if语句的多余空白行,影响最终 HTML 的整洁度。Go 模板提供了简单的语法来控制:
{{-:在{{后加一个-,表示移除此标签前面的空白字符(包括换行)。-}}:在}}前加一个-,表示移除此标签后面的空白字符。
模板注释
Go 模板的注释语法是 {{/* 注释内容 */}}。这些注释在模板执行时会被完全忽略,不会输出到最终结果中。
{{/* 这是一个模板注释,不会显示在 HTML 中 */}}
<p>Hello</p>